Graph Learing for Crowd Navigation
Robot crowd navigation based on Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) and Deep Reinfocement Learning.
*This part serves as supplements for some information which is not included in my thesis paper. For more detailed information, please refer to the thesis (only Chinese version). I conduct this research as my undergraduate thesis and receive excellent thesis award at SUSTech.
Motivation
Imagine you’re in the mall, you’ve just bought a heavy TV on sale, and you need help getting it to your car. Suddenly, a robot comes along, offering to carry it for you. Or perhaps, you’re at the airport running late for your flight, with your luggage trailing behind you. Wouldn’t it be great if a robot could smoothly navigate the bustling crowd and take care of your bags?
Currently, humans, with excellent sense of judgment and intuition, can effortlessly navigate through crowded places like malls or airports, instinctively knowing which direction to take, how much space to maintain from others, and even when to overtake that slow-moving person in our way. But for robots, it’s a whole different ball game. For starters, robots don’t have access to the intent or destination of other moving entities, making it tough for them to predict their paths. Plus, the way humans adapt their movements based on other moving or stationary objects is difficult to model.
So, my research aims to make robots efficient, safe, and autonomous navigators in crowded spaces, avoiding collisions and interacting optimally with humans and obstacles. This can lead to more efficient human-robot collaboration in real-world scenarios, turning robots into powerful tools for us.
Algorithm Design
Two key methods are used for better perfomance in Crowd Navigation task. First, a graph structure is used to model the problem scenario. In this graph, robots or humans are represented as nodes, and their interactions as edges. The relations between all agents can be reasoned and those important state representations can be computed by Graph Convolutional Networks, or GCNs for simplicity. As shown in the visuals of Interaction Modeling module, the thickness of the lines in the graph are fetched from relation inference which indicates the strength of influence between two individuals.
Secondly, a trajectory prediction module is built to forecast humans’ future states, which is trained by supervised learning. By forecasting a human’s future path, robots can make long-term decisions to avoid future collisions and plan efficient routes.
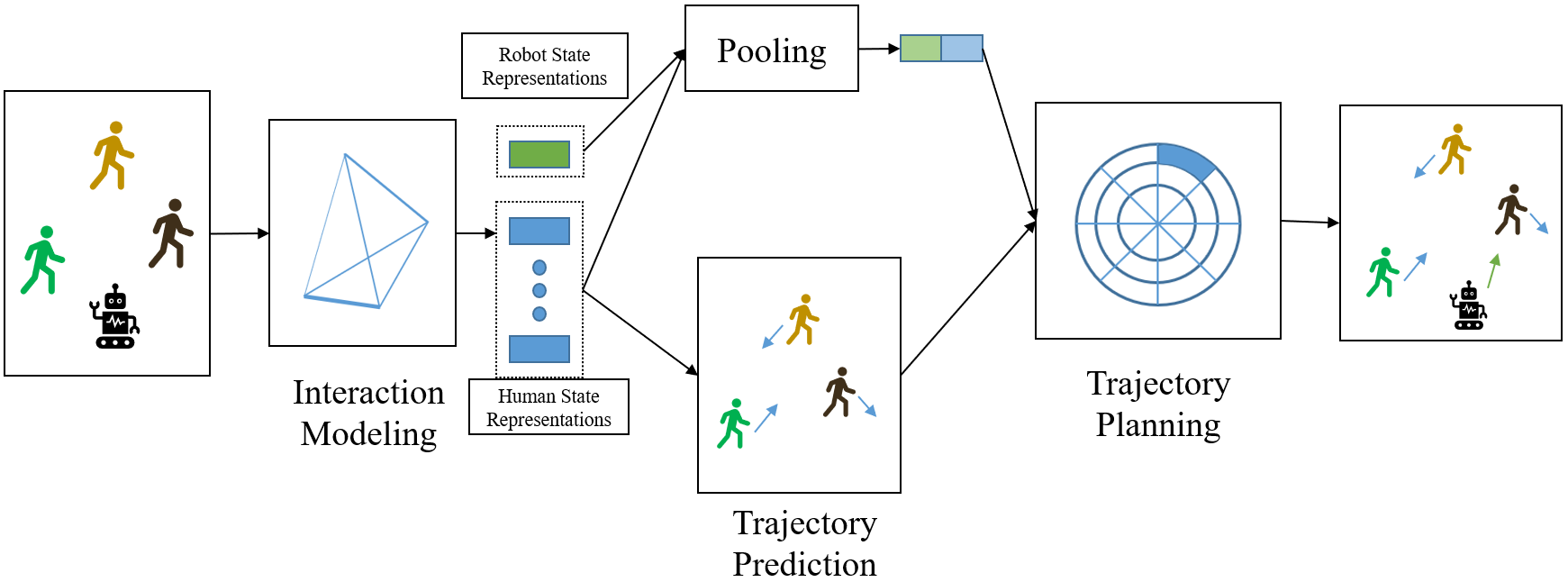
With the understanding of these interactions and the prediction of human trajectories, a state-value network trained by reinforcement learning can calculate and measure the robot’s action space, finding the most beneficial and safest path to its destination.
Supplements
About the hardware test, I design the first generation robot as shown in the following pictures.
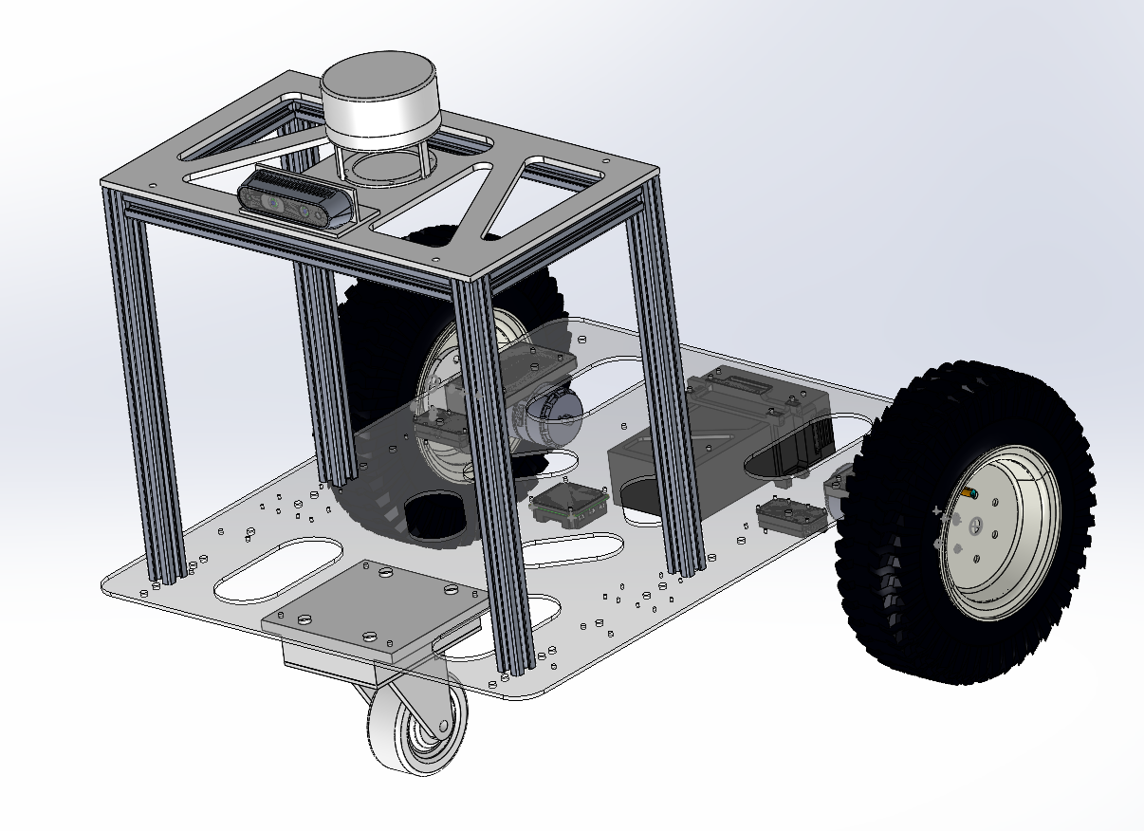
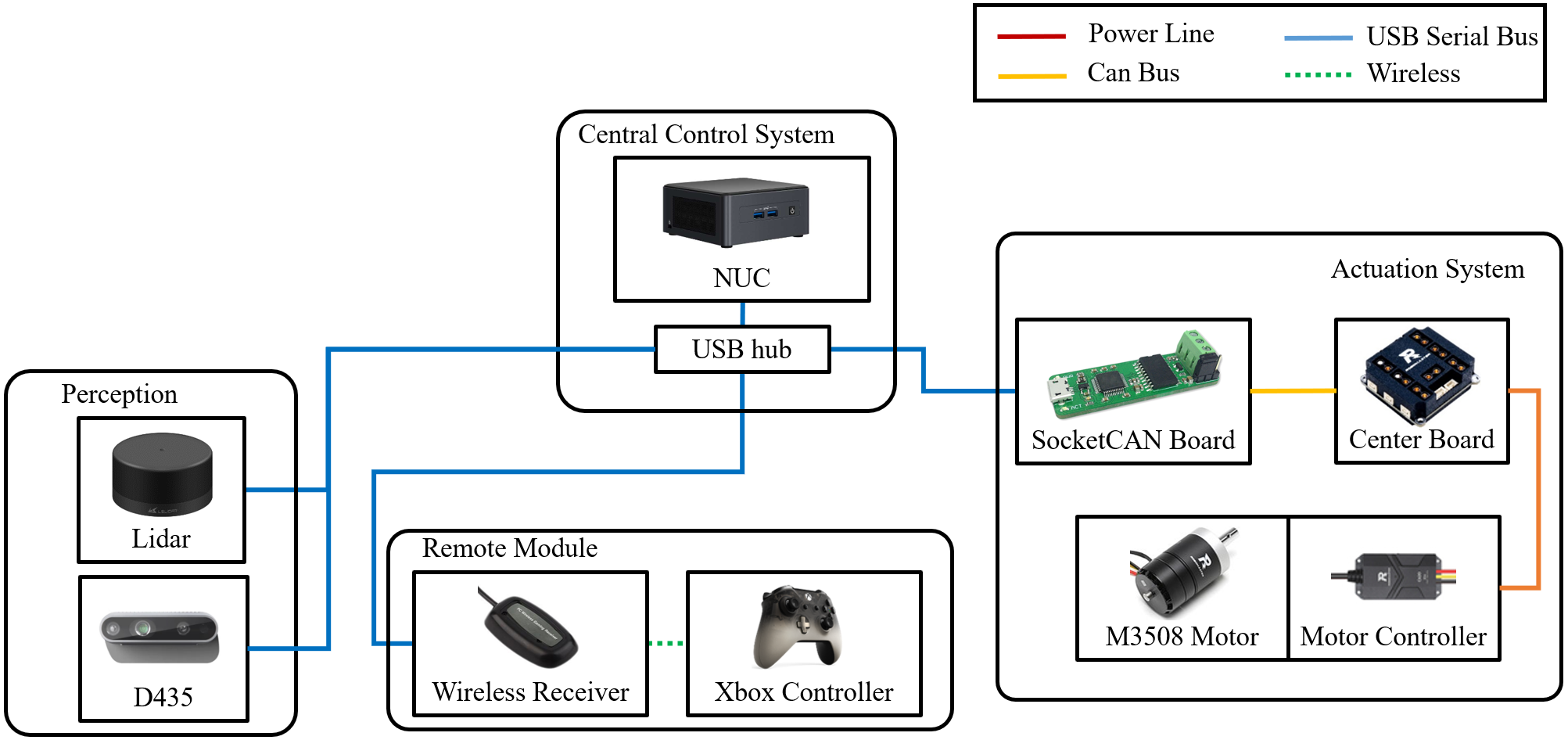
However, considering the hardware cost about the first generation robot, I choose use spark robot to conduct experiments.
